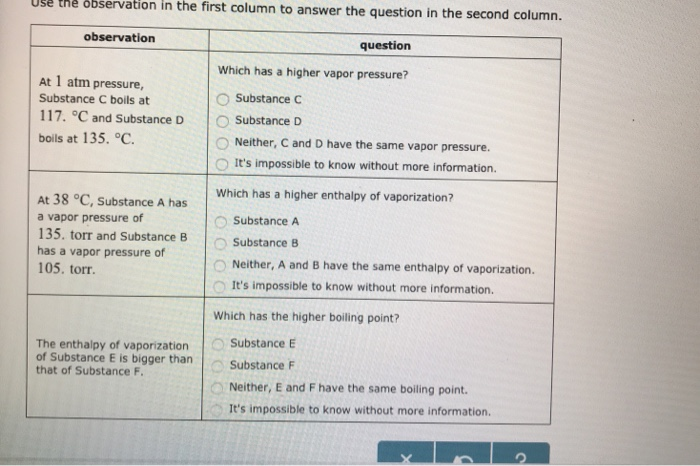
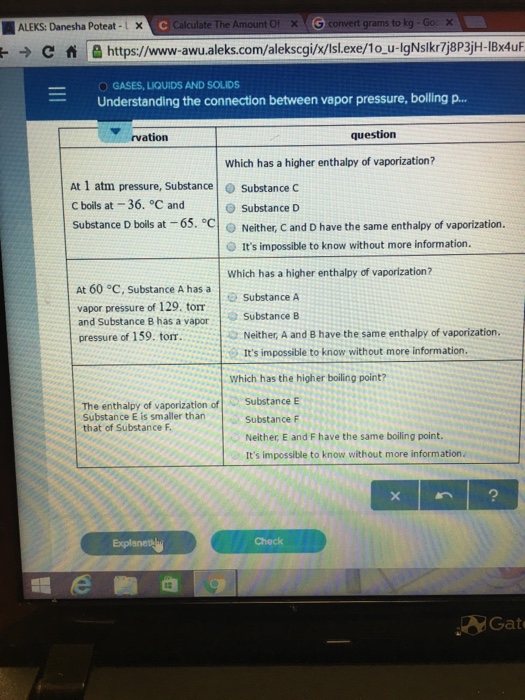
At Pressure Substance C Boils At And Substance D Boils At
It's impossible to know without more information.
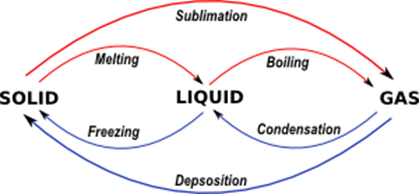
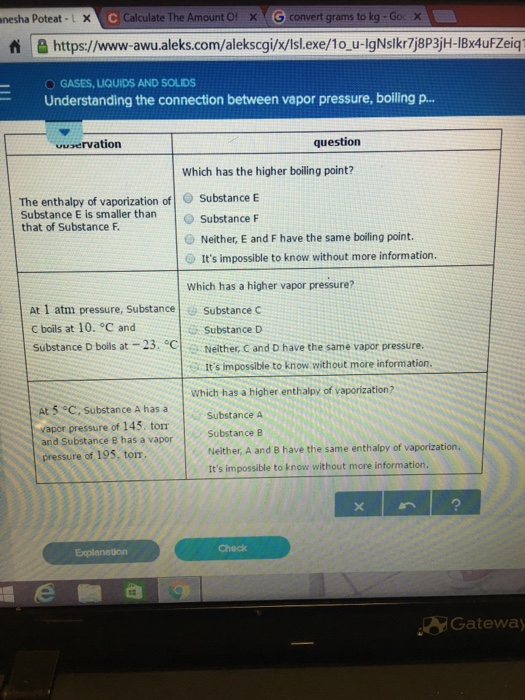
At pressure substance c boils at and substance d boils at. Substance E Substance F Neither, A and B have the same boiling point. Explain why the boiling point of the ether is so much lower than the boiling point of ethanol. The boiling point of a substance is the temperature at which the vapor pressure of a liquid equals the pressure surrounding the liquid and the liquid changes into a vapor.
1 "When water boils at 212 F boils, it is only absorbing latent heat.". The boiling point is defined as the temperature at which the vapour pressure of the liquid is equal to the ambient pressure, and bubbles of vapour form directly in the liquid. Increasing the air pressure on the water b.
It's impossible to know without more information. The vapor pressure of a substance depends on the temperature. Xe, H 2, H 2 O, LiCl, H 2 S.
Determine the vapor pressure (in mm Hg) of a substance at 29°C, whose normal boiling point is 76°C and has a ΔHvap of 38.7 kJ/mol.?. At 5 degree C, Substance A has a vapor pressure of 145, torr and Substance 8 has a vapor pressure of 195 torr. You also need the melting point (m.p.).
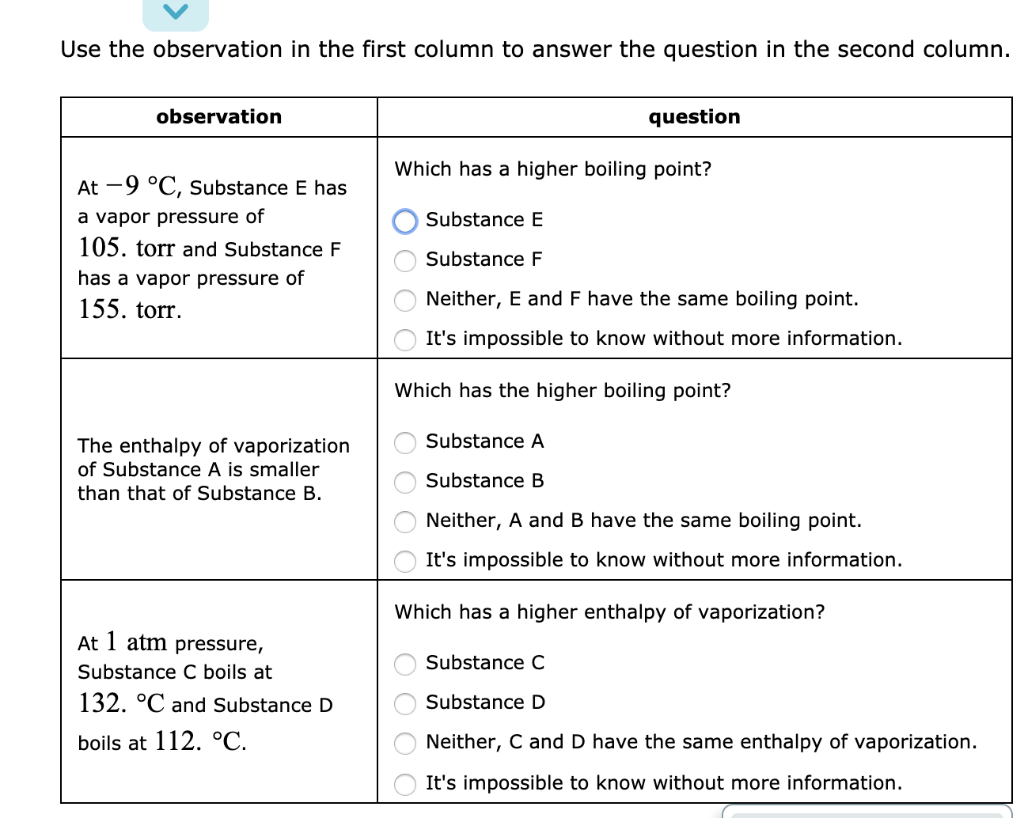
A substance has a standard boiling point of 78.90 °C. (b) the temperature above which the substance cannot exist as a liquid regardless of the pressure. Freezing point is less than melting point for a pure substance b.
The approximate normal boiling point of this substance is:. The boiling point of a liquid varies depending upon the surrounding environmental pressure. It's Impossible to know without more information.
C) Point C corresponds to the liquid phase of the substance. Which has a higher boiling point?. If the boiling point (b.p.) is below room temperature, it’s a gas.
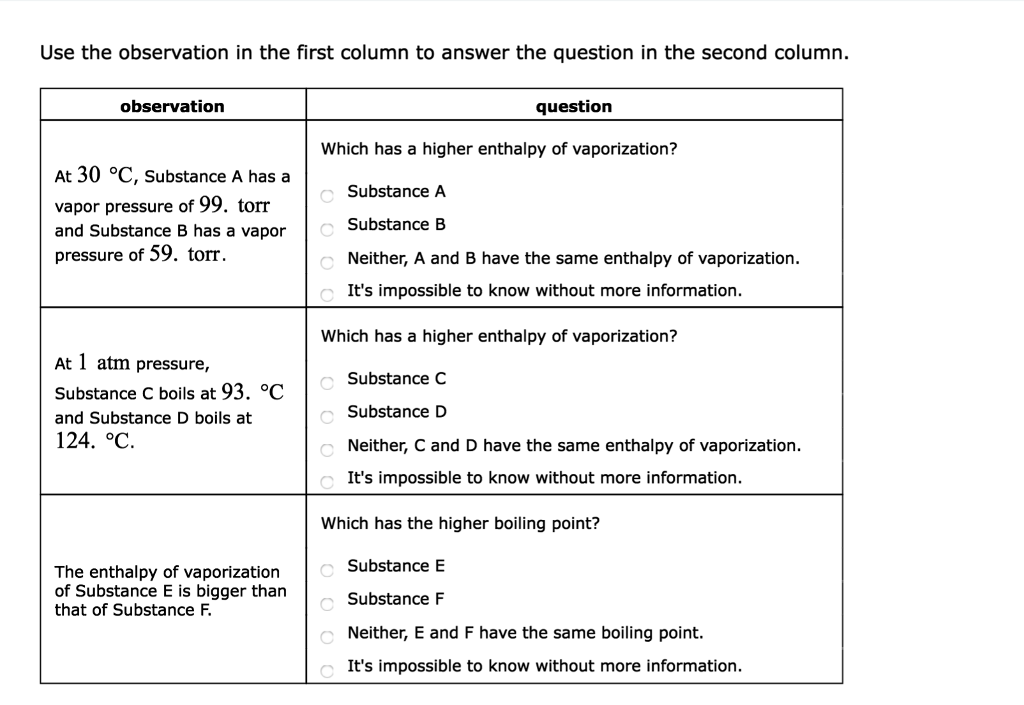
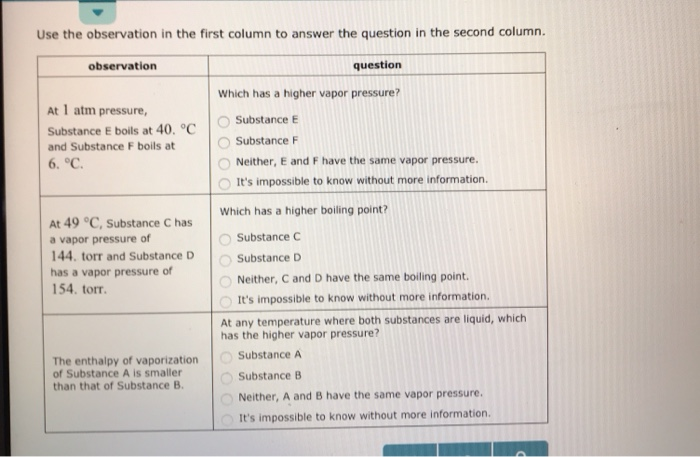
Substance E Substance F Neither, C and D have the same boiling point. Torr It's impossible to know without more information. Atmospheric pressure in inches of mercury (" Hg) decreases by _____ inch(s) per 1000 feet increase in elevation.
E) Raising the pressure from point E to point C causes the substance to condense. C) the temperature at which water boils. The normal boiling point is specified when the ambient pressure is 1 ⋅atm.
Dimethyl ether boils at −23.7°C. B) the temperature at which the vapor pressure of a substance equals 1 atm. At 17 degree C, substance C has a vapor pressure of 125.
Evaporation can occur at any temperature, but takes place only at the surface of the liquid. At higher altitudes the air pressure is lower. Which has the higher boling point?.
Substance C Substance D neither, C and D have the same boiling point. Arrange these substances in order of INCREASING boiling point:. Solutions and Vapor Pressure.
This pressure decreases with increasing elevation and hence the boiling point of a liquid also decreases. The same substance has a vapor pressure at −21.09 °C of 0.101 bar. Boyle's law, also referred to as the Boyle–Mariotte law, or Mariotte's law (especially in France), is an experimental gas law that describes how the pressure of a gas tends to increase as the volume of the container decreases.
Is above room temperature, and the m.p. A modern statement of Boyle's law is:. At 1 atm pressure, Substance C boils at 10.
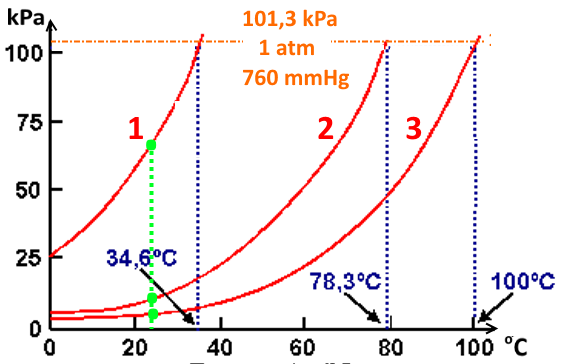
This means that the vapor pressure of water is 1 atm or 760 mmHg at 100 оC. Applying a great deal of heat. Since it exists as a gas at room temperature, it obviously has a low boiling point, the lowest of the group, which is -1°C.
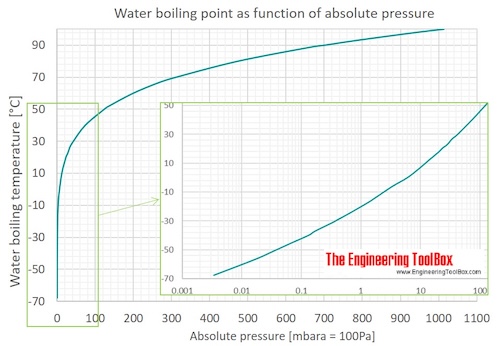
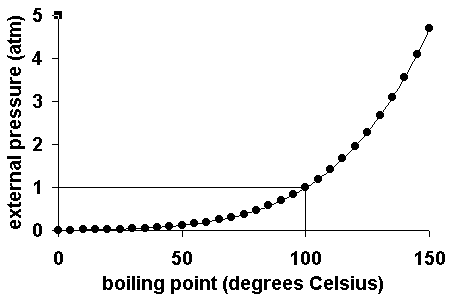
For example, for water, the boiling point is 100ºC at a pressure of 1 atm. Boiling begins _____ b. Water boils in a pressure cooker c.
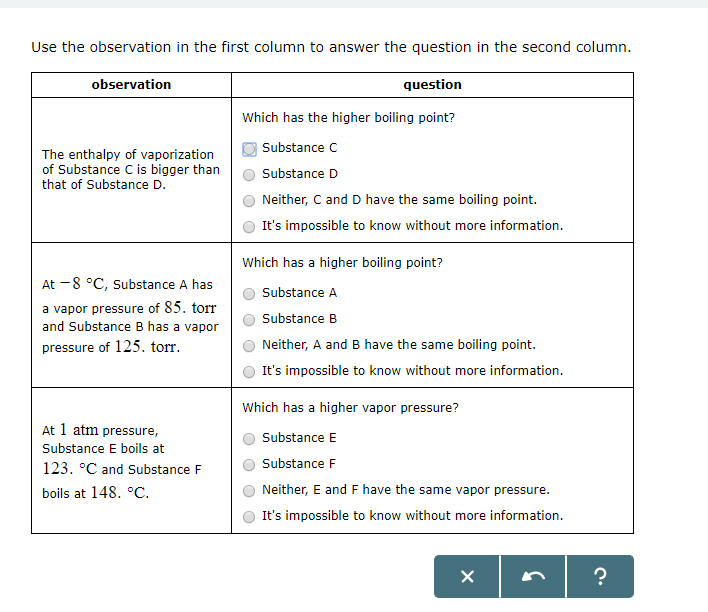
The triple point occurs at approximately 165 K. The change of phase of a substance from liquid to gas is known as evaporation. Substance C Substance D Neither, C and D have the same enthalpy of vaporization.
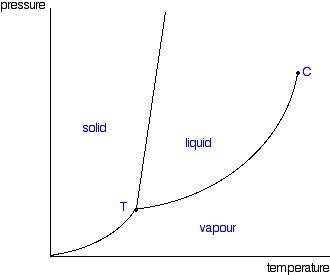
From ideal gas equation we have, Where n is the Number of moles and R is the gas. Decreasing the pressure on the water d. In thermodynamics, the triple point of a substance is the temperature and pressure at which the three phases (gas, liquid, and solid) of that substance coexist in thermodynamic equilibrium.
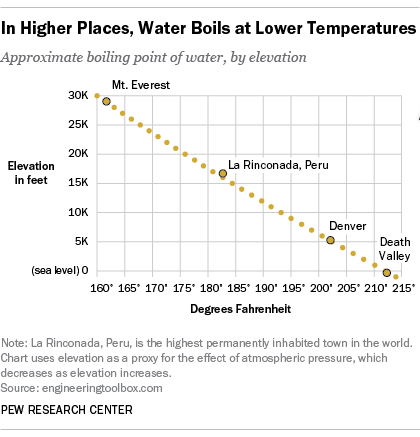
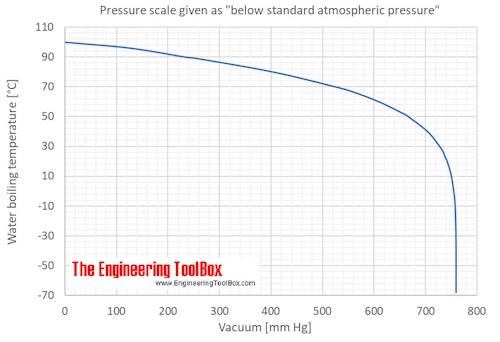
We expect water to boil at 100 o C when we cook, but in Denver, Colorado, which is a mile high and has a lower atmospheric pressure than at sea level, water boils at a lower temperature. A) vapor pressure is exactly 1 atmosphere. The normal boiling point is defined as.
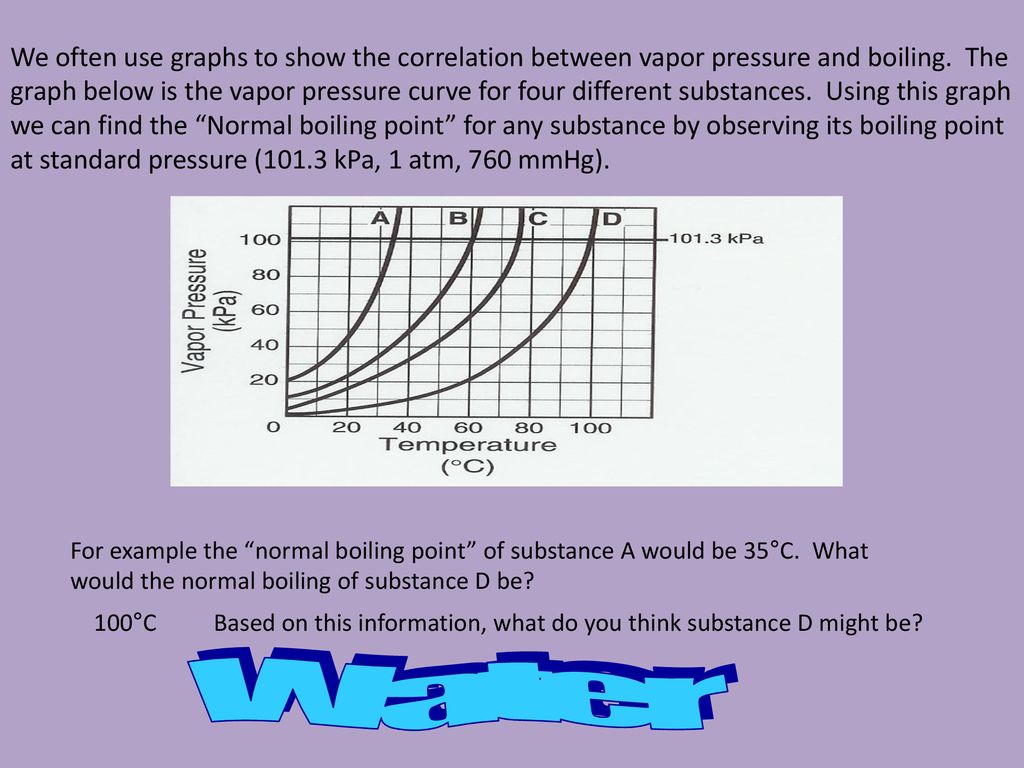
Their structural formulas are, respectively, CH 3CH 2OH and CH 3OCH 3. D) temperature is greater than room temperature. 1)freeze 2)boil 3)melt 4)condense 8.When the vapor pressure of a liquid is equal to the atmospheric pressure, the liquid will 9.The graph below shows the relationship between vapor pressure and temperature for substance X.
The onset of boiling occurs when the vapour pressure inside the bubble equals the external pressure that acts to collapse it. Because the boiling point of a liquid rises with pressure, the contents of the pressurized vessel can remain liquid so long as the vessel is intact. All boiling points below are normal/atmospheric boiling points:.
B) vapor pressure is equal to, or greater than, the external pressure pushing on it. It is that temperature and pressure at which the sublimation curve, fusion curve and the vaporisation curve meet. The inverse as you decrease the pressure the temperature required to boil is also reduced.
Substance C Substance D Neither, C and D have the same enthalpy of vaporization. 7 psia and 760 mm Hg - (o F, o C)-3. Melting begins _____ c.
Torr and Substance D has a vapor pressure of 186. Solution for If the pressure of a substance is increased during a boiling process, will the temperature also increase or will it remain constant?. D) At a higher temperature and pressure than point D, the substance exists as a supercritical fluid.
The solid line between points B and C is identical to the plot of temperature dependence of the vapor pressure of the liquid. Weight of the substance C. The boiling point decreases as the vapour pressure increases.
D) the pressure at which a liquid boils at 273.15 K. A) the pressure of a gas when its temperature reaches 373.15 K. A pure substance has well-defined physical properties such as freezing and boiling points.
ΔH vap = 24. At a pressure of 1.5 atm, the. Boils are painful, red bumps on the skin that are caused by bacteria.
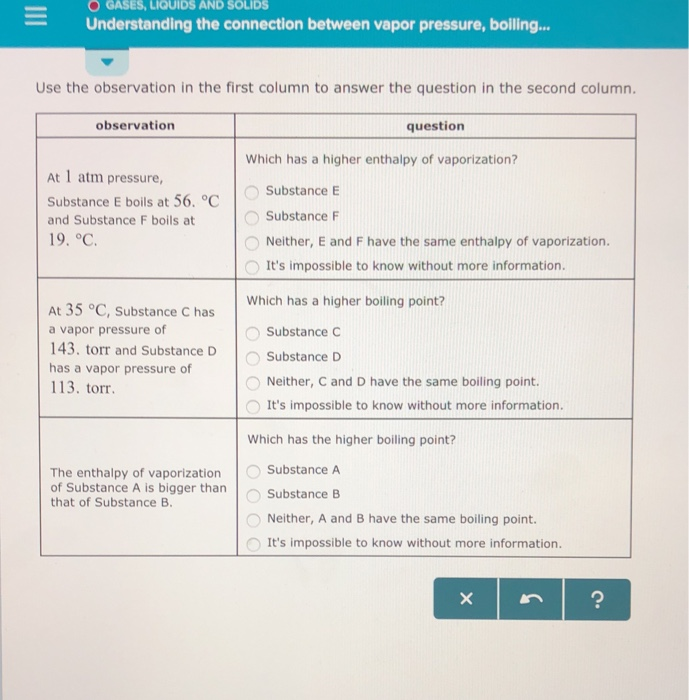
If the temperature is raised from 50 K to 400 K at a pressure of I atm, the substance boils at approximately 185 K. Is below room temperature, it’s a liquid. Question Which has a higher enthalpy of vaporization?.
2,47 x 1023 kJ/mol C. The vapor pressure of a substance is measured over a range of temperatures. Observation At 25 degree C, Substance C has a vapor pressure of 136.
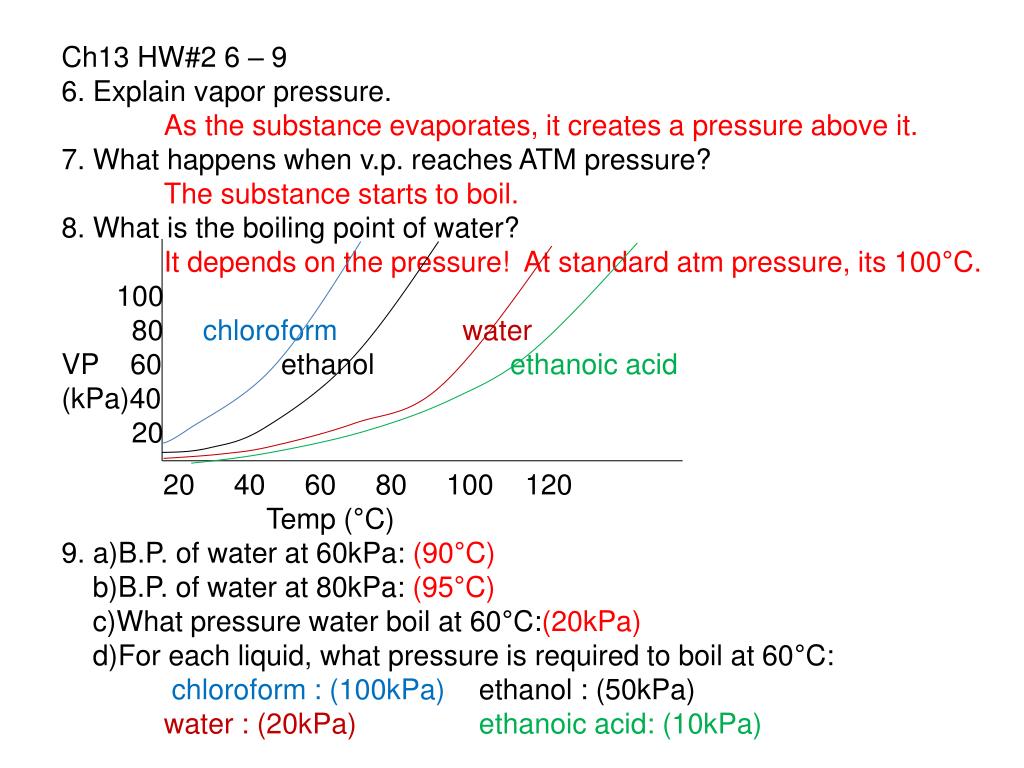
To achieve a vapor pressure of 0.6 atm, substance D must be heated to about 60˚C 25. If the pressure of a substance is increased during a boiling process, will the temperature also increase or will it remain constant?. C) D) E) answer 6) The vapor pressure of any substance at its normal boiling point is 6) A) 1 torr B) equal to the vapor pressure of water C) equal to atmospheric pressure D) 1 Pa E) 1 atm 7) Some things take longer to cook at high altitudes than at low altitudes because _____.
Increasing the external pressure requires a greater matching vapour pressure that is only provided at a higher vapour (and liquid) temperature as the molecules mean speed is increased. The normal boiling point for A is about 60˚ d. Learn how to get rid of a boil and what you can do at home and with your doctor to treat and prevent future boils.
Both freezing point and melting point are the same for a pure substance. Determine the normal boiling point of a substance whose vapor pressure is 55. Is above room temperature, it’s a.
C) temperature is equal to 273 K (standard temperature). E) the sum of the enthalpies of vaporization and fusion at 298 K. What would happen to the boiling point if the liquid were tested at higher altitude?.
Ethanol boils at 78.4°C. Torr Which has a higher boiling point?. The liquid phase of this substance cannot exist under conditions of 2 atm at any temperature.
Using the following phase diagram of a certain substance, in what phase is the substance at 50°C and 1 atm. What is the enthalpy of vaporization in kJ mol−1?. Degree C and Substance D boils at - 23.
At 1 atm pressure, Substance C boils at -36 degree C and Substance D boils at -65 degree C Which has a higher enthalpy of vaporization?. A liquid boils when its. A liquid boils when the vapor pressure above a liquid equals the atmospheric pressure.
When you have a liquid (in 1 atmosphere of air pressure) we define its boiling point when its vapor pressure is equal to atmospheric pressure. Water could be made to boil at 105°C instead of 100°C by _____. Of course, if we reduce the ambient pressure, the boiling point will be substantially reduced, and this is an example of the principle of vacuum distillation, where an otherwise involatile liquid is distilled under high vacuum.
The vapor pressure of a substance is related to temperature, so increasing the temperature increases the vapor pressure till it =1 atmosphere and starts boiling. Freezing begins _____ d. The boiling point of a liquid depends on temperature, atmospheric pressure, and the vapor pressure of the liquid.
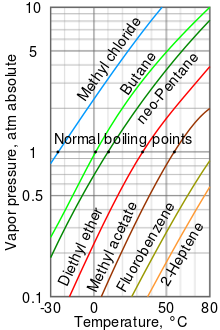
For the vapor pressure/temperature diagram shown, approximate the normal boiling points for:. Torr and Substance B has a vapor Substance B Neither, A and B have the same boiling point. What is the enthalpy of vaporization of the substance?.
To understand it more clearly, recall that the boiling point of water is 100 оC at 1 atm. The normal boiling point of a liquid is (a) the temperature at which the vapor pressure equals 760 torr. (c) the temperature at which the gas molecules have more kinetic energy than the molecules in the liquid.
A plot of the natural log of the vapor pressure versus the inverse of the temperature (in Kelvin) produces a straight line with a slope of -42.5 K. In contrast, many properties of a solution depend on the concentration of solute.Properties of solutions that depend on the concentration (but not on the identity) of solute are called colligative (collective) properties.You will learn how the concentration of a solute. At 59 °C, Substance A has a Substance A vapor pressure of 85.
These molecules exert a pressure on the walls of a closed container. (c) HBr (d) HI (e) H 2 SO 4. A liquid in a partial vacuum has a lower boiling point than when that liquid is at atmospheric pressure.
What will the vapor pressure be at 25.00 °C?. Foreign ions introduced to water a. Torr and Substance D has a vapor pressure of 115.
The atmospheric pressure at sea level is equal to 101,325 Pa (pascal). 7) A) natural gas flames don't burn as hot at high altitudes. The boiling point of a pure liquid _____ as external pressure decreases.
When the atmospheric pressure is equal to the vapor pressure of the liquid, boiling will begin. Determine the vapor pressure (in mm Hg) of a substance at 29°C, whose normal boiling point is 76°C and has a Hvapof 38.7 kJ/mol. The boiling point of a substance is the temperature at which the vapor pressure of the liquid is equal to the surrounding atmospheric pressure, thus facilitating transition of the material between gaseous and liquid phases.
It contains all of the combinations of temperature and pressure at which the liquid boils. At every point along this line, the liquid boils to form a gas and the gas condenses to form a liquid at the same rate. Boiling Point, 75-79 °C/12 mmHg.
The vapour pressure is the pressure exerted when the molecules leave the surface at the same rate as they return. Internal volume of the substance B. Degree C Which has a higher vapor pressure?.
So,if the pressure of a substance is increased during a boiling process then temperature is also getting change. Is reached when v.p. LiF - As noted, this is the highest boiling point substance at 1676°.
The absolute pressure exerted by a given mass of an ideal gas is inversely proportional to the volume it occupies if the. A boiling liquid expanding vapor explosion (BLEVE, / ˈ b l ɛ v iː / BLEV-ee) is an explosion caused by the rupture of a vessel containing a pressurized liquid that has reached temperatures above its boiling point. Freezing point is greater than melting point for a pure substance c.
296 g = 0. Which has a higher enthalpy of vaporization?. Decreasing the air pressure above the water c.
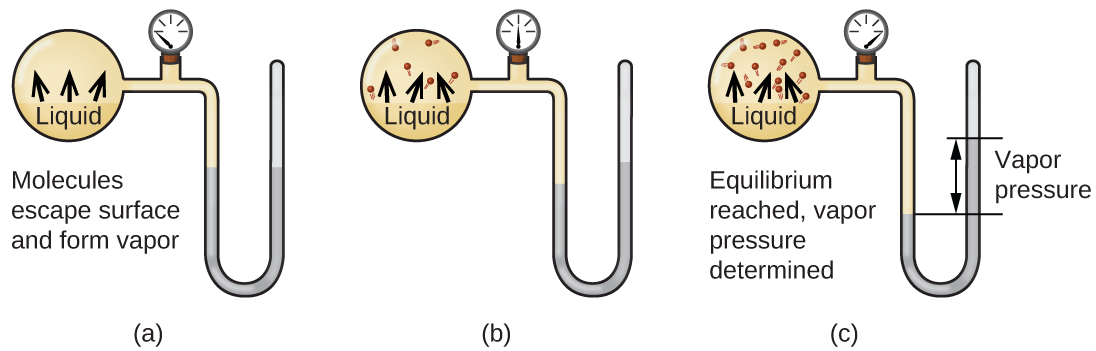
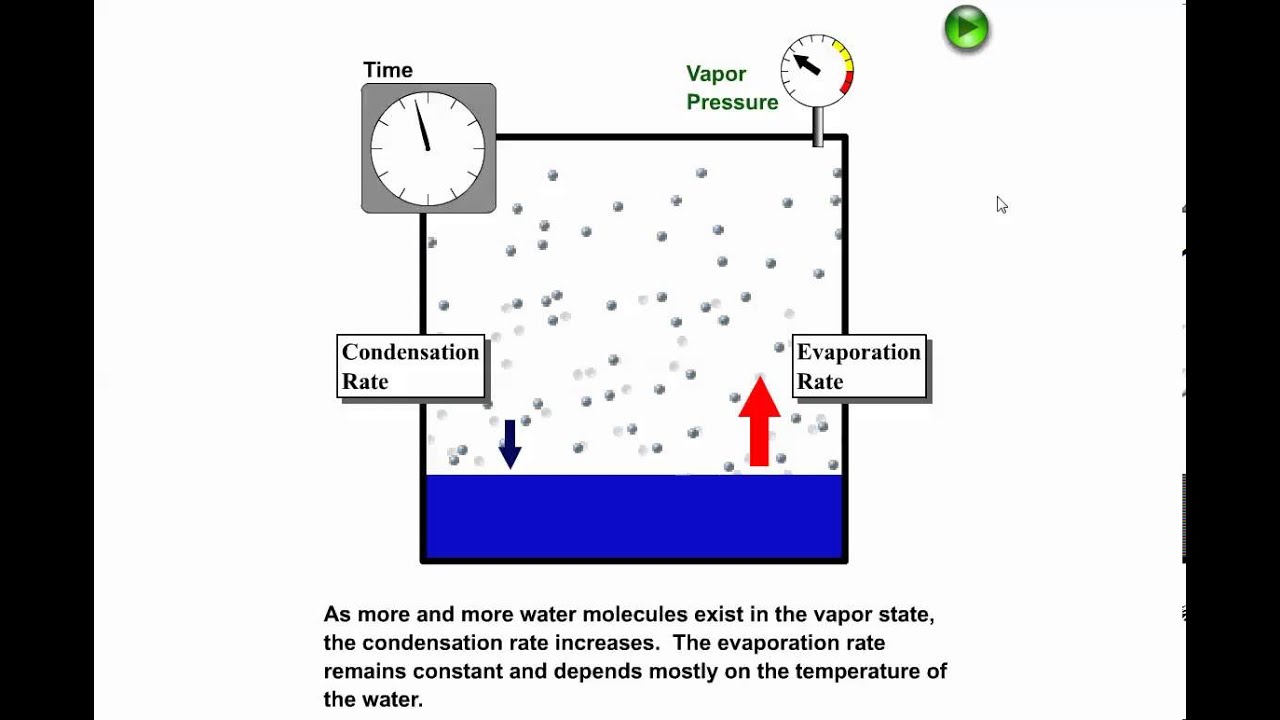
Air pressure above the substance. Both of these d. > Vapour Pressure Some of the molecules at the surface of a liquid have enough kinetic energy to escape into the atmosphere.
The vapor pressure of most liquids has a fairly predictable temperature-dependence, so from one boiling point measurement it is possible to give a good estimation of the boiling point at other pressures (or boiling pressure at other temperatures). It's impossible to know without more information. For example, the triple point of mercury occurs at a temperature of −38.440 °C (−37.
They give the temperature at which the vapor pressure of. The boiling point is the easier concept to think about. (image on other side) A) 430K B) 180 K C) 190 K D) 300 K.
Time-lapse entry of liquid into the capillary tube. _____ Figure 2 E Liquid Gas Solid Liquid Solid Liquid Gas A B80 C D F G Energy e 0 40 60 40 60 100 Temperature (°C) CHCl 3 CCl 4 H 2 O Figure 1 101.325 kPa ). Does the substance give off or take in heat as it goes from D to C?.
The vapor pressure would have to increase to equal the higher atmospheric pressure for the substance to boil.

Chemistry 1 Using The Clausius Clapeyron Equation To Solve For Vapor Pressure Youtube

Answered When Two Chemicals Have The Same Bartleby

B I I Ii C I Ii M D I I Ii Q 62 To 64
At Pressure Substance C Boils At And Substance D Boils At のギャラリー

Oneclass 1 Define Triple Point A The Temperature That Is Unique For A Substance B The Temperatu
Solved Use The Observation In The First Column To Answer Chegg Com

Phase Diagrams
Ppt Chapter 13 States Of Matter Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id

Answered The Phase Diagram Of A Substance Is Bartleby

Physical Chemistry Solutions D Elevation In Boiling Point 39 The Vapour Pressure Of Benzene At A Certain Temperature Is 640 Mm Kunduz
/glass-saucepan-on-a-gas-burner-with-boiling-water-dor961844-5a036e3089eacc0037b4abb1.jpg)
Boiling Definition In Chemistry

What Are The Freezing Melting And Boiling Points Of Solids Liquids And Gases Owlcation Education

A Water Freezes At Standard Pressure B Water Is At Its Triple Point C

Boiling Point Wikipedia
Characteristics Of The Solid Liquid And Gaseous States
Solved Use The Observation In The First Column To Answer Chegg Com
Http Cdochemistrychristman Pbworks Com W File Fetch Ap
Boiling Of A Liquid Substance

Boiling Point Definition Examples Temperature Facts Britannica

Answered If A Substance Has Stronger Bartleby

Tb Chapter11 bbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbb

Distillation

The Wizard Test Maker Revsworld
Solved The Enthalpy Of Vaporization Of Substance E Is Sma Chegg Com
Solved Use The Observation In The First Column To Answer Chegg Com

Oneclass 1 What Type Or Types Of Intermolecular Forces Are Present Between Linear Molecules Of H Ce

Ppt Chapter 13 States Of Matter Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id

Boiling Point Elevation And Freezing Point Depression Video Khan Academy
Www Lamar Edu Arts Sciences Files Documents Chemistry Biochemistry Dorris 1412exam2 Pdf

Effect Of Pressure On The Boiling Point Of Water Youtube

Attractions And Boiling

Melting Point Wikipedia

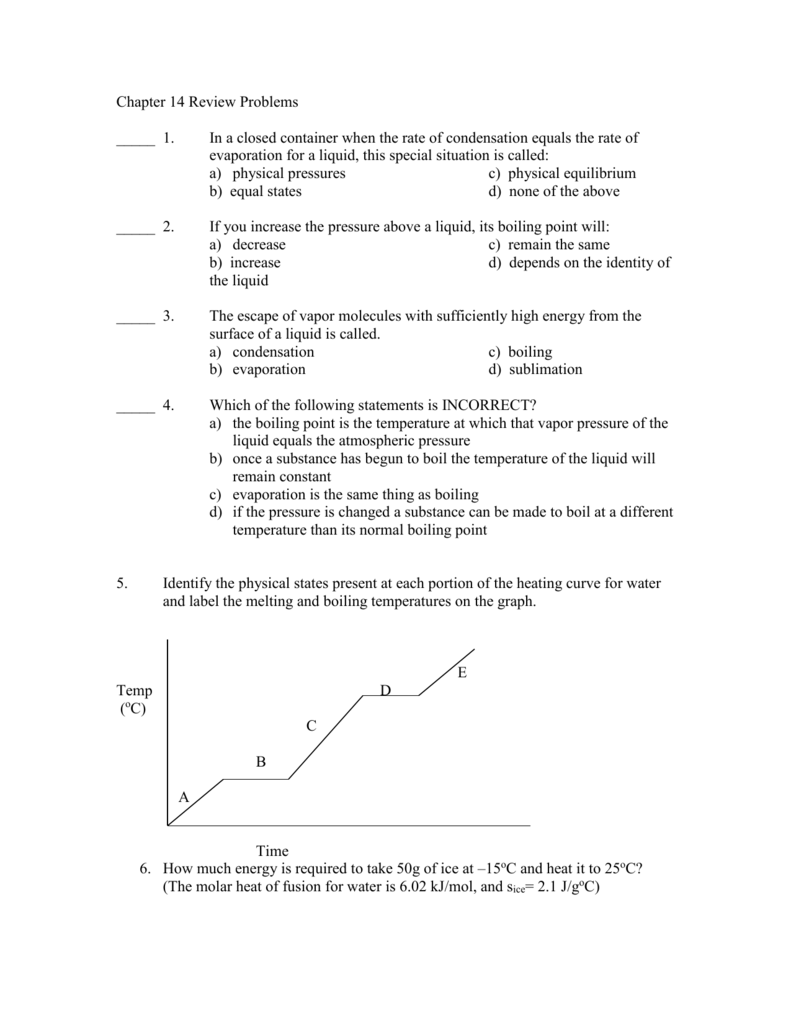
Heating Curve For Water Introduction To Chemistry

For The First Three Questions Use The Key Below
Water Boiling Points At Vacuum Pressure
Boiling
Phase Diagrams Of Pure Substances
Solved At 1 Atm Pressure Substance C Boils At 36 Degree Chegg Com

Solved Which Has A Higher Enthalpy Of Vaporization At 1 Chegg Com
Does Water S Boiling Point Change With Altitude Americans Aren T Sure Pew Research Center

Aleks Calculating Vapor Pressure From Boiling Point And Enthalpy Of Vaporization Youtube
Solved Use The Observation In The First Column To Answer Chegg Com

Vapor Pressure Video States Of Matter Khan Academy
Solved Use The Observation In The First Column To Answer Chegg Com
Solved Gases Liquids And Solids Understanding The Connec Chegg Com
Vapor Pressure Wikipedia

Aleks Predicting The Relative Boiling Points Of Pure Substances Youtube

Tb Chapter11 bbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbb
10 3 Phase Transitions Chemistry Libretexts
A Vapor Pressure Lowering
Boiling Point Wikipedia

Chemistry 1 Using The Clausius Clapeyron Equation To Solve For Vapor Pressure Youtube
Usflearn Instructure Com Courses 9868 Files Download Wrap 1
Water Boiling Points At Vacuum Pressure

Vapor Pressure Curves Ck 12 Foundation

Solved Use The Observation In The First Column To Answer Chegg Com
Chapter 14 Review Problems
Properties Of Liquids
Tb Chapter11 bbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbb

A Solution Containing 3 3 G Of A Substance In 125 G Of Benzene B Pt 80 Oc Boils At 80 66 Oc If Kb For Benzene Is 3 28 K Kg Mol 1 The Molecular
Define Melting Point And Boiling Point What Is The Difference Quora

Use The Observation In The First Column To Answer The Question In The Second Column Observation Homeworklib
Q Tbn And9gcslxxohf6s Byidgpakdcgmarcsqcauhrjvta Usqp Cau
Loganchemistry Weebly Com Uploads 2 4 7 4 Ch 13 Review Answers Pdf

Mcq Questions Latent Heat Melting Point
Www Plps K12 Org Site Handlers Filedownload Ashx Moduleinstanceid 24 Dataid 3863 Filename Practice test chapter 10 key Pdf
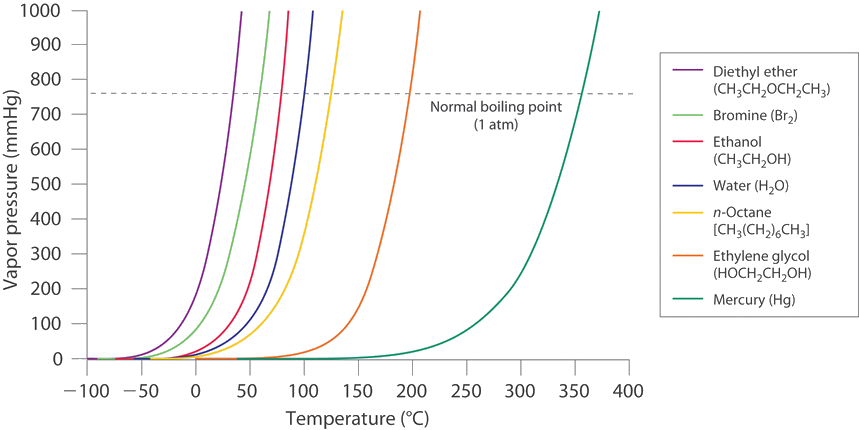
11 5 Vapor Pressure Chemistry Libretexts

15 2d Understanding The Connection Between Vapor Pressure Boiling Point And Enthalpy Of Vaporizati Youtube

Key Chapter 11 Practice Test
Solved Use The Observation In The First Column To Answer The Question In The Second Column Which Has A Higher Vapor Pressure At 1 Atm Pressure S Course Hero

Solved Use The Observation In The First Column To Answer Chegg Com
Http Www2 Chem Uic Edu Tak Chem Solutions set 10 Pdf

Boiling Chemistry Libretexts

Change Of State Of A Matter Melting Fusing Evaporation Condensation

Boiling Point Accessscience From Mcgraw Hill Education

Boiling Point Elevation Wikipedia

Solved Use The Observation In The First Column To Answer Chegg Com

Changes Of State Ppt Download
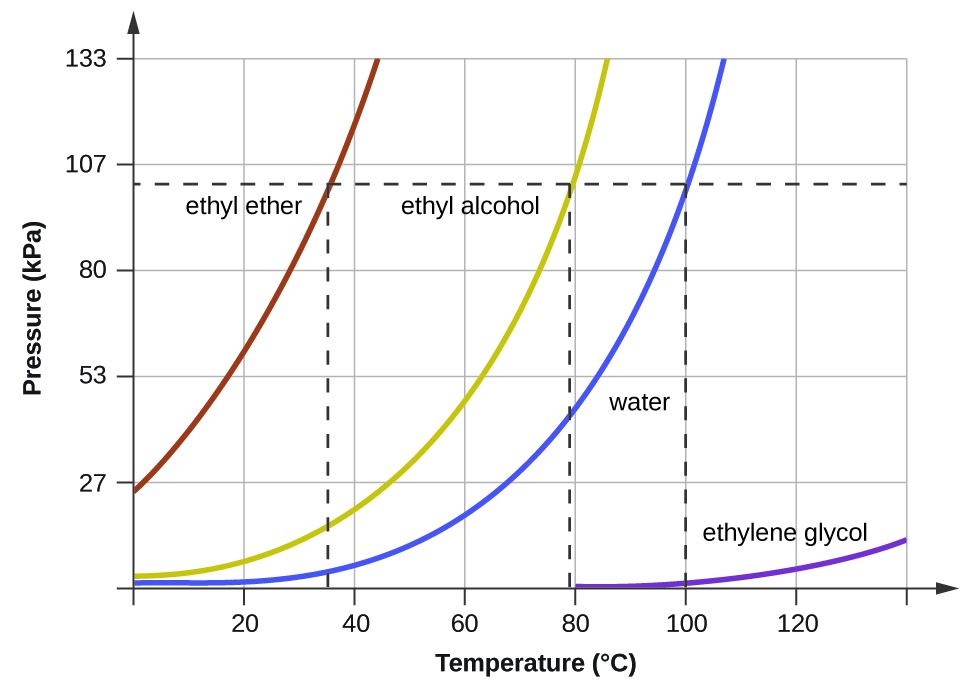
10 3 Phase Transitions Chemistry Libretexts

Chapter 2a Pure Substances Phase Change Properties Updated 9 09

Solved Use The Observation In The First Column To Answer Chegg Com

An Aqueous Solution Of A Non Volatile And Non Electrolytic Substance Boils At 100 5 C Calculate The Osmotic Pressure Of This Solution At 27 C Ko For Water Per 1000 G 0 50

Oneclass Heat Of Vaporization Substance Would You Expect To Have The Highest 3 Pts A F2 B C12 C
2

Melting Point Freezing Point Boiling Point
Properties Of Liquids

Question 3 I A Design An Experiment To Show That Ammonium Chloride Undergoes S A Diagram Give Two Science Matter In Our Surroundings Meritnation Com
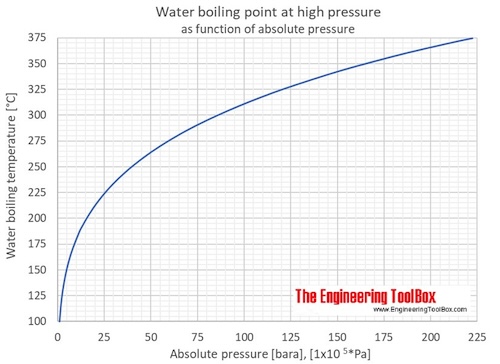
Water Boiling Points At Higher Pressure

An Aqueous Solution Of A Non Volatile And Non Electrolytic Substance Boils At 100 5 C Calculate The Osmotic Pressure Of This Solution At 27 C Ko For Water Per 1000 G 0 50
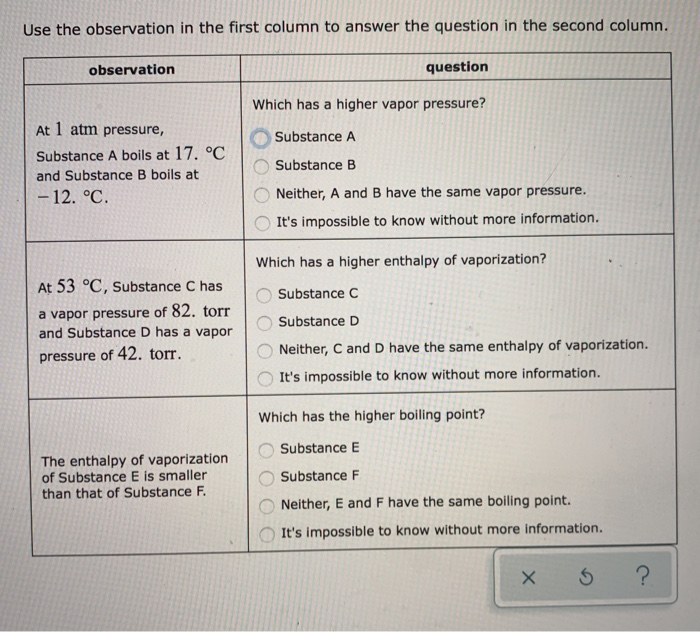
Solved Use The Observation In The First Column To Answer Chegg Com

The Boiling Point Of A Substance Is Affected By A The Mass Of The Substance B The Substance S Brainly Com

Gases Liquids And Solids Understanding The Connection Between Use The Observation In The First Column Homeworklib

Tb Chapter11 bbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbb

Boiling Chemistry Libretexts

Distillation

Boiling Point Wikipedia

Tb Chapter11 bbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbb
Changes Of State Ppt Download
Characteristics Of The Solid Liquid And Gaseous States

Which Of The Following Solutions Will Have Highest Boiling Point
Phase Changes Boundless Chemistry




